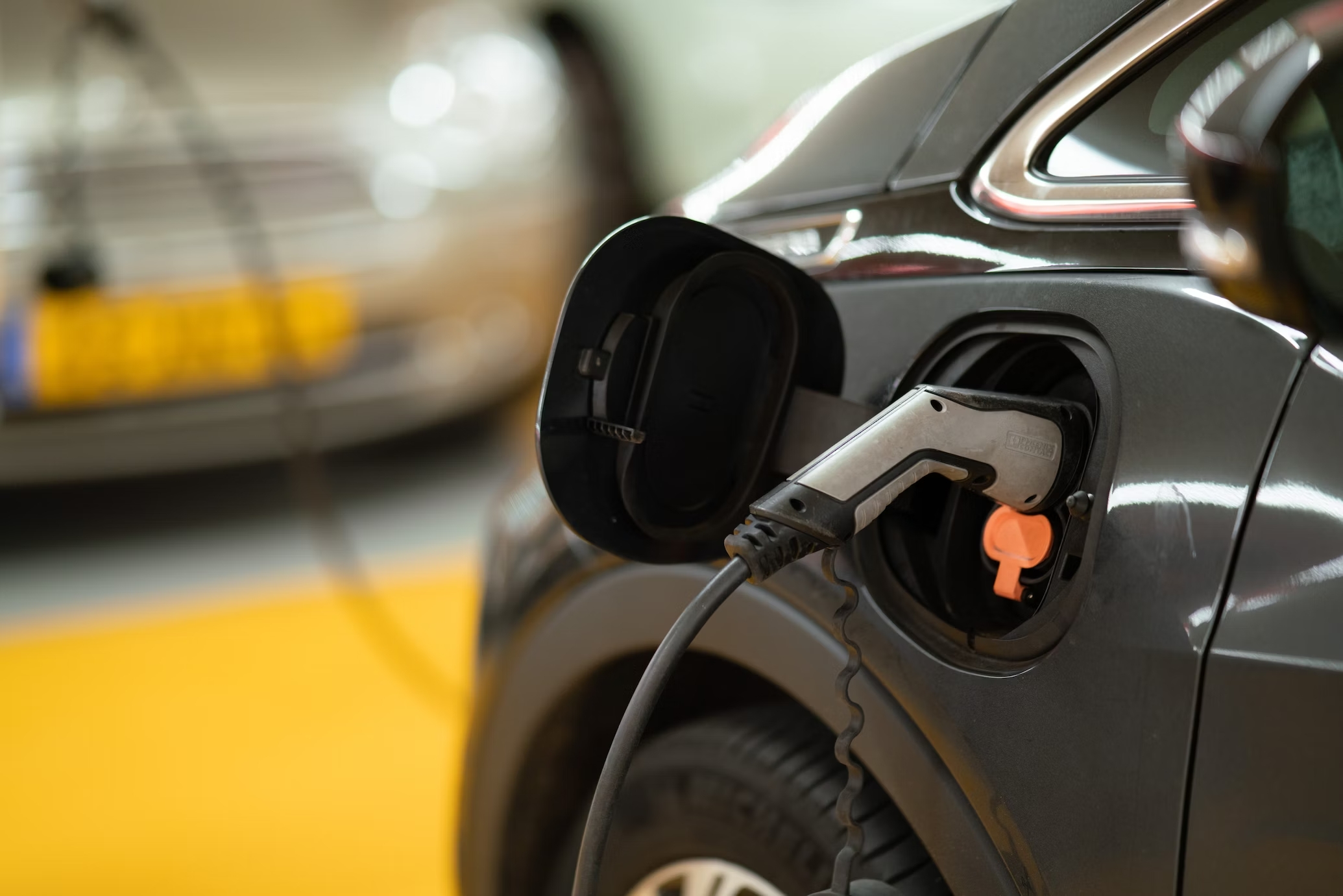
Here in the El Monte area and all across California, electric vehicles (EVs) are becoming more and more popular. If you’re considering purchasing an EV, it’s a good idea to understand in advance where and how to charge it. If this is your first EV, you might be used to filling up at the pump, so the possible convenience of charging at home could be an exciting new experience. Read on to learn more about the different types of EV chargers and connectors and how you might be able to charge your EV at home.
How Does EV Charging Work?
There are three EV charging methods: Level 1, Level 2, and direct current (DC) fast charging.
Level 1 Charging
Level 1 charging is the simplest and slowest method of charging an EV. With Level 1 charging, approximately 3 to 5 miles of range are added per hour of charging. More than a day would typically be needed to fully charge an EV’s battery with Level 1 charging. Any EV can be plugged into a standard 120-volt wall outlet for Level 1 charging; you do not need any additional equipment.
Level 2 Charging
Compared with Level 1 charging, Level 2 charging is much faster. With Level 2 charging, approximately 20 to 25 or more miles of range are added per hour of charging. An overnight charge is usually sufficient to fully charge an EV’s battery with Level 2 charging. Level 2 charging requires having an electrician install a particular charging station with a dedicated 240-volt electrical circuit. All EVs can use Level 2 chargers. These types of charging stations may be found in public areas or in some homes.
DC Fast Charging
Although you might sometimes hear DC fast charging referred to as Level 3 charging, that name is not technically correct. DC fast charging is the quickest method of EV charging available. This method requires a 480-volt connection, and not every EV can use DC fast charging. These types of charging stations may be found in some public areas. Approximately 10 miles of range are added per minute of charging. A 20- to 60-minute charge would be sufficient to charge a typical EV’s battery to roughly 80 percent capacity.
Charging Curve
When you plug in an EV to charge the battery, you might notice that the battery quickly gains charge until it is about 80 percent full. After this time, the charging rate slows down. This variation of speed at which the battery charges is called the “charging curve.” The curve differs from one EV to another and can change depending on battery temperature or weather conditions. It can be helpful to keep the charging curve in mind if you’re charging your vehicle in the middle of a road trip or in a public station where others are waiting.
Connectors
There are several types of EV connectors. The type of connector your vehicle has may determine which charging stations you can use.
- SAE J1772: This connector typically comes standard with your vehicle and is the most common type of connector in use. The SAE J1772 connector can use Level 1 and Level 2 chargers.
- SAE Combined Charging System (CCS) or J1772 CCS Combo: This connector allows the EV to plug into a DC fast charging system.
- CHAdeMO: This connector is found in many Nissan and Mitsubishi vehicles and is also used for DC fast charging, similar to the CCS connector.
- Tesla Connector: The Tesla connector is only used in Tesla vehicles for Level 1, Level 2, and DC fast chargers.
Can EVs Be Plugged In Anywhere?
EVs can be charged in many places, including homes, workplaces, and public areas. However, certain types of charging stations might be limited to specific locations.
Charging at Home
A standard 120-volt wall socket is sufficient for Level 1 charging. This means that you can charge your EV at any home. Because Level 1 charging is the slowest method, you might also choose to install a 240-volt line at home for Level 2 charging. If you charge your EV at home, the price of the electricity used should appear on the homeowner’s electricity bill. This means that you may want to consider charging during off-peak times if your electric company offers discounted rates.
Charging at Work
Your workplace may offer Level 2 EV charging stations for employees. If this is the case, leaving your vehicle to charge during your working hours may be convenient.
Charging in Public and on the Road
Public EV charging stations, often Level 2, may be found where people are likely to park cars, such as parking garages and lots. DC fast charging may also be available. Depending on the charging station, there may be a fee to charge your vehicle, or it might be free to use. If you’re driving in a new place or taking a long trip, it’s a good idea to determine where you can charge your EV on the go.
Is At-Home Equipment Compatible With Charging Electric Cars?
Yes, at-home equipment is compatible with charging electric cars. The charging speed will depend on whether Level 1 or Level 2 charging is used. Because a standard wall outlet is sufficient for Level 1 charging, no additional equipment is needed to use Level 1 charging at home. If you want to use Level 2 charging at home, a Level 2 charger needs to be installed by an electrician. This will require a 240-volt outlet. DC fast charging is not available in homes.
Ready To Test-Drive an EV?
At Longo Toyota, we are happy to help you with anything you need when considering EVs. Our knowledgeable team is happy to answer all of your questions and help you find the best EV for you. You can also browse our inventory if you’re interested in a hybrid vehicle or a vehicle with a gas-powered engine. Come and see us at 3534 North Peck Road in El Monte, or give us a call at 626-539-2113.
Black and silver car steering wheel by Michael Fousert is licensed with Unsplash License